When Is It Too Late To Repair A Completely Torn Tendon?
Original Editor- Jim Druwé
Top Contributors - Ilona Malkauskaite, Kim Jackson, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane, Shreya Pavaskar, Jim Druwé, Laurent Chapelle, Claire Knott, Wanda van Niekerk, Admin, Rachael Lowe, Evan Thomas, Naomi O'Reilly and Daphne Jackson
Introduction [edit | edit source]
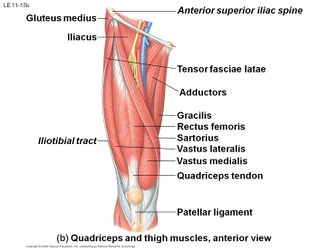
Quadriceps tendon tear is an injury that occurs when the tendon that attaches the quadriceps musculus (a grouping of 4 muscles in the front part of the femur) to the patella or kneecap tears. The quadriceps tendon may be partially or completely torn.[1] Quadriceps tendon rupture is a rare but serious injury. If this injury is not promptly recognized and early on operated, it may pb to inability.[ii]
Clinically Relevant Anatomy [edit | edit source]
The quadriceps tendon comes from the muscular junction of the, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis and vastus intermedius, at the anterior superior pole of the patella.[three] The tendon is multilayered. The rectus femoris is the most superficial layer inserting on to the patella and the vastus lateralis and medialis are the middle layers.[4] The quadriceps tendon in combination with patellar tendon and the patella bone make upwards the extensor mechanism of the lower leg. These muscles derive their neurovascular innervation from the femoral nerve and artery. Specifically, the rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, and vastus lateralis proceeds their arterial supply from the lateral femoral circumflex artery. The vastus medialis gains its arterial supply from the femoral artery, superior medial genicular branch of the popliteal avenue, and the profunda femoris artery. The vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and the vastus intermedius human action both as knee joint extenders too as help with patellar tracking. The vastus lateralis is the largest of the quadriceps muscles. It helps to pull the patella laterally. This activeness must exist counterbalanced by the vastus medialis, which is the smallest of the quadriceps muscles and acts to pull the patella medially. The vastus intermedius acts to help stabilize midline tracking of the patella. The combined contraction of this group of inductive thigh muscles causes extension of the lower leg. The rectus femoris too plays a role in hip flexion. A rupture of this central tendon drastically hinders knee extension and directly effects functionality. The caste that a quadriceps tendon rupture limits lower leg extension is based on the severity of tendon impairment. Minor tendon tears may have minimal impact on extensor part, while consummate tendon tears may totally impede lower leg extension.[3]
Epidemiology [edit | edit source]
Lower leg extensor mechanism ruptures every bit a whole are very rare, simply are reported to accept high morbidity and are oftentimes debilitating. Quadriceps tendon tears are reported to have an incidence of 1.37/100,000 and 0.68/100,000 for patellar tendon tears. Extensor mechanism ruptures are most common unilaterally.[3]Fractional and complete tears occur predominantly in males. Ruptures of the quadriceps tendon occur relatively infrequently and ordinarily occur in patients older than 40 years. Simply these ruptures may be seen in well-nigh any age grouping.[4]
- usually occurs in patients > 40 years of age
- males > females (up to viii:ane)
- occurs in nondominant limb more than twice as frequently
Etiology [edit | edit source]
Quadriceps tendon tears have a positive correlation with historic period and multiple medical comorbidities. This injury historically is more prevalent in males, with the historic period afterward xl years. This is in opposition to patellar tendon tears, which commonly occur before age forty, and are often related to sports injuries. [3]
A muscle rupture often happens during a high impact action with a bad landing. During a landing there is a heavy load on a knee in flexion and the human foot is planted on the footing (jump). The Quadriceps musculus makes a rapid, eccentric contraction. Other mechanism is caused by a force straight on the anterior side of the knee (fall). Patients typically present with astute genu pain, swelling, and functional loss post-obit a stumble, autumn, or giving mode of the human knee.[4]
Chance factors [edit | edit source]
Nigh quadriceps tendon tears happens considering the tendon is weakened.[5]
- Tendinitis: inflammation of the tendon causes weakening and maybe fifty-fifty niggling strains.
- A poor blood supply to the tendon due to diseases also weakens the tendon.
Chronic diseases
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism which causes bone resorption which causes weakening of the fibro-cartilaginous junction between the tendon and bone tissue.
- Chronic renal failure [6] [7]; this can crusade connective tissue elastosis which is suggesting for a weakening of the tendon.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), gout, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, obesity, infections and metabolic diseases have a negative effect on the strength of the tendons.
Drugs abuse besides accept/has a degenerative effect on muscle tendon:
- Corticosteroids usage has been linked to an increase of muscle and tendon weakness.
- Fluoroquinolones, a special antibiotic is related to tendon ruptures.[8]
Other factors such as knee surgery and immobilization as well increase the adventure, considering the strength and flexibility of the muscle and tendon decreases.
Characteristics/ Clinical Presentation [edit | edit source]
Information technology tin exist classified as partial or complete rupture. There is oft a popping or tearing feeling at the time of outcome. Some patients are able to walk post-obit this injury, only many cannot. The patient will be unable to direct the knee joint without assist when the tendon is completely ruptured. About of the patients nowadays with acute knee pain, swelling and there is a palpable defect at the site of the tear. Y'all tin feel a dent/gap merely proximal of the patella (the suprapatellar expanse) where the quadriceps tendon was torn. The quadriceps will exist sensitive and cramping. In that location is a hematoma visible around the knee. Ordinarily, obvious suprapatellar swelling, ecchymosis, and tenderness are present. The patella may sag or droop as a consequence of the quadriceps tendon tear but swelling may obscure this finding. There is a function loss especially in that location volition exist a loss of extension and also loss of stability. If the patient is not seen in the astute phase, diagnosing the rupture becomes more difficult, and it can be easily missed. Many patients are idea to have only simple articulatio genus sprains during their examination in the emergency room and are not given advisable, immediate follow-upwards. [four]
Differential Diagnosis [edit | edit source]
Differential diagnosis include:
- Patellar tendon rupture
- Patella stress fracture
- Femoral shaft stress fracture
- Os or soft tissue tumor
- Compartment Syndrome
- Referred lumbar spine pain
- Meralgia Paresthetica
- Femoral nerve injury or entrapment.[1]
Upshot Measures [edit | edit source]
The Lysholm and Tegner-score and the ROM of the knee were used to decide the progress and result of the rehabilitation and have been proven consequent, responsive and reliable. [9]
Examination [edit | edit source]
During the inspection you tin can meet swelling around the suprapatellar area, there is a hematoma.
When you lot start the active examination you tin immediately run across that at that place is functional loss. Patients may accept frequent buckling of the knee and difficulty with stair climbing. Patients may be able to ambulate but will practise so with a gait demonstrating genu stiffness and elevation of the hip to suit the swing-through stage.
Testing for full, agile extension against gravity is the most important aspect of the exam. The patient will be unable to perform a straight leg heighten. Extension lags of varying degrees are seen, depending on the amount of retinacular impairment. In incomplete ruptures, the patient may be able to fully extend the human knee from the supine position but non from the flexed position. If only tendinitis is present, no extension lag should exist noted with whatever test position. It is also important that you examine the contralateral knee to rule out bilateral rupture.
Results of neurologic examination are normal except for decreased quadriceps motor function and an absent patellar reflex. [iv] In that location is also the quadriceps tendon rupture diagnose test of Jolles BM et al. which is an minimal invasive an easy bachelor technique. [10]
Physical examination -
- tenderness at site of rupture
- palpable defect commonly within 2 cm of superior pole of patella
- unable to extend the knee against resistance
- unable to perform direct leg raise with complete rupture
Imaging is commonly not indicated in quadriceps tendon injuries. However, ultrasound may have some clinical utility. Ultrasound can be used to find a tendon defect, and to assess the degree of tendon gap with articulatio genus flexion. Ultrasound has also been used serially to assess healing and to make up one's mind the presence of associated hematomas, effusions, or calcifications. Radiographs are usually non helpful in making this diagnosis but may have some clinical utility in ruling out other associated injuries or conditions. Radiography may be helpful in determining patella position. A superior patella may be indicative of a patellar tendon rupture, while an junior patella may be suggestive of a quadriceps tendon rupture. Apparently radiography may besides rule in or out associated patella avulsions or other associated patellar fractures. MRI may exist used preoperatively but is unremarkably non necessary due to advances in musculoskeletal ultrasound. [i]
Surgical Management [edit | edit source]
When in that location are only partial ruptures the genu must be immobilized (3-6 weeks), surgery is mandatory when the tendon is completely torn and is best started as early on as possible (latest 72h after injury), then the tendon can exist reattached to the patella, after the surgery the knee is immobilized for 4-vi weeks.
Physiotherapy Direction [edit | edit source]
Immediately later on the injury, the RICE treatment (Balance, Ice, Compression, Tiptop) can be started. Partial tear are ordinarily treated with ultrasound and TENS (Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation), heat and ice therapy, muscle strengthening, proprioception exercises and transmission therapy (massage, passive extension, flexion).
To rehabilitate a complete tendon rupture you tin cull betwixt the conservative or a more aggressive treatment afterwards surgery. The bourgeois treatment consisted of 4 to 6 weeks of immobilization in ten° of flexion. 2 days after surgery intensive isometric quadriceps exercises can kickoff. During the immobilization period, the weight bearing will be increased then full weight begetting will be reached after six weeks , then will be started with mobilizations to regain the full range of motion of the articulatio genus [xi]. The more aggressive handling which is not appropriate for every patient, consists of immediate mobilization and after 7 to 10 days full weight bearing, quadriceps settings, heel slides, massage, heel prop, talocrural joint pumps. Caryatid-gratuitous ambulation was reached after 7 to eight weeks, which lead to a faster rehabilitation.[12] [13] [14] [fifteen]
Examples of exercises to be used:
Prognosis [edit | edit source]
Rehabilitation of quadriceps tendon tears have good outcomes, Gender, mechanism of injury, tear location, time to diagnosis and repair weren't relevant to the outcomes. Most patients regained their full ROM, muscle forcefulness, sports participation and Activities of Daily Living.[16]
Hurting and swelling decrease over fourth dimension, and quadriceps function can improve.
Athletes treated for partial or complete ruptures may render to play when several conditions are met, including the post-obit:
- The patient should have nearly full, painless ROM;
- Knee strength should exist at least 85-ninety% of the other knee;
- Completion of a sport-specific agility program is highly recommended for athletes involved in vigorous sports, such as football, basketball, soccer, or tennis.[17]
Studies more often than not have reported proficient results following early on repair of consummate unilateral and bilateral quadriceps tendon ruptures. The type of repair, the location of the tear, the patient'south historic period and sexual activity, and the machinery of injury do not appear to affect the results. Expert ROM usually can be regained, simply some persistent quadriceps weakness is fairly common. Most patients can return to their previous occupation, simply many cannot render to their pre-injury activity level.[xviii]
Clinical Lesser Line [edit | edit source]
Rehabilitation of quadriceps tendon tears have skillful outcomes, Gender, mechanism of injury, tear location, time to diagnosis and repair weren't relevant to the outcomes. Virtually patients regained their total ROM, muscle strength, sports participation and ADL.[16]
Resource [edit | edit source]
- Rectus Femoris
- Vastus Medialis
- Vastus Lateralis
- Vastus Intermedius
- Patella
- Patellar tendon tear
References [edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 one.1 1.2 https://world wide web.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/quadriceps-tendon-tear/ (accessed 14 Januar 2022).
- ↑ Popov I, Ristić V, Maljanović M, Milankov 5. Quadriceps tendon rupture - treatment results.Med Pregl 2022;66(11-12):453-8.
- ↑ 3.0 three.1 3.2 3.3 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482389/ (accessed xiv Januar 2022).
- ↑ iv.0 iv.1 4.2 4.3 4.four James Edin Lyle et al.; quadriceps tendon rupture; Medscape; 2022. Bear witness level:C
- ↑ Shah M.One thousand.; Simultaneous bilateral rupture of quadriceps tendons: assay of risk factors and associations; South Med J.; 2002 Aug;95(8):860-866; Bear witness level:B
- ↑ Kim Y.H. et al.; Spontaneous and simultaneous rupture of both quadriceps tendons in a patient with chronic renal failure; KneeSurg Sports TraumatolArthrosc; 2006; 14: 55–59. Evidence level:D
- ↑ Kricun R. et al.; patellar tendon rupture with underlying systemic disease; AJR ; 1980 October; 135: 803-807. Testify level: D.
- ↑ Van Der Linden P.D. et al.; Tendon Disorders Attributed to Fluoroquinolones: A Study on 42 Spontaneous Reports in the Period 1988 to 1998; Arthritis care & research; 2001; 45: 235–239. Testify level: C.
- ↑ Briggs K.K. et al.;The reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the Lysholm score and Tegner activity scale for anterior cruciate ligament injuries of the knee: 25 years subsequently.;Am J Sports Med.; 2009 May. Evidence level: 2A.
- ↑ Jolles B.M. et al.; A new clinical test in diagnosing quadriceps tendon ruptures; Ann R CollSurgEngl; 2007; 89: 259-261.Evidence level:D.
- ↑ Gaheer R.S. et al.; Rapid recovery from spontaneous and simultaneous bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture in an active, healthy individual; Orthopedics.; 2022 July; xiii;33(seven):512. Evidence level:D.
- ↑ West J et al.; Early Motion Afterward Quadriceps and Patellar Tendon Repairs: Outcomes With Unmarried-Suture Augmentation; The American Journal of Sports Medicine; 2008 February, 36 (2): 316-323. Testify level: C.
- ↑ Yilmaz C. et al.; Tendon lengthening repair and early on mobilization in treatment of neglected bilateral simultaneous traumatic rupture of the quadriceps tendon; Knee Surg Sports TraumatolArthrosc.; 2001 May; 9(3):163-166. Evidence level:D.
- ↑ Levy K. et al.; A method of repair for quadriceps tendon or patellar ligament (tendon) ruptures without bandage immobilization.Preliminary report; ClinOrthopRelat Res.; 1987 May;(218):297-301.Prove level:D.
- ↑ James Edin Lyle et al.; quadriceps tendon rupture; Medscape; 2022.Evidence level:B.
- ↑ 16.0 16.ane O'Shea K. et al.; Outcomes post-obit quadriceps tendon ruptures; Injury.; 2002 April ;33(3):257-260.Evidence level: B.
- ↑ James Edin Lyle et al.; quadriceps tendon rupture; Medscape; 2022.Evidence level:B.
- ↑ Vigneswaran N, Lee K, Yegappan M, spontaneous bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture, case report, Singapore Med J, 2007.Show level: 4.
Source: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Quadriceps_Tendon_Tear
Posted by: hickdeaverm.blogspot.com


0 Response to "When Is It Too Late To Repair A Completely Torn Tendon?"
Post a Comment